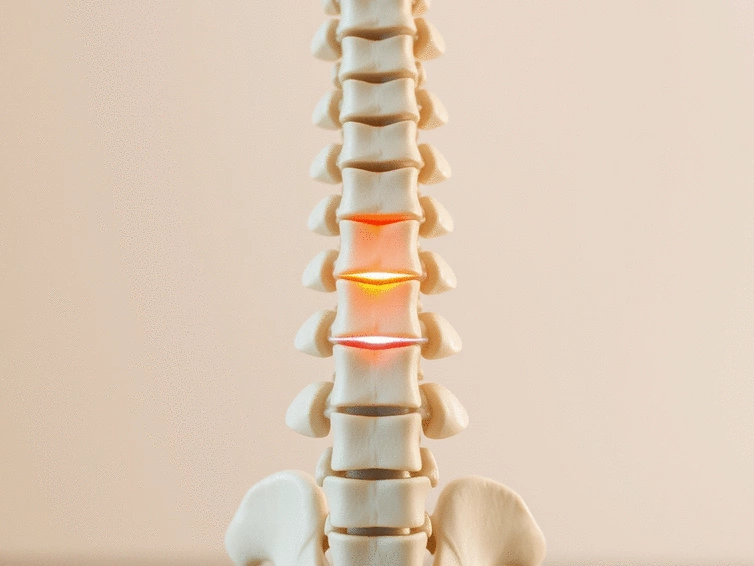
Understanding Degenerative Disc Disease
Have you ever felt a persistent ache in your back that just won’t go away? Understanding the underlying causes can empower you to take control of your health. This article dives into the world of Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) and its connection to sciatica, shedding light on crucial aspects that can help you manage your symptoms effectively.
What You Will Learn
- Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is a natural consequence of aging, not a disease, affecting spinal health.
- Understanding the structure and function of intervertebral discs is essential for maintaining a healthy spine.
- Lifestyle factors like poor posture, sedentary behavior, and obesity can accelerate spinal degeneration.
- DDD can lead to sciatica by causing nerve compression through mechanisms like disc herniation and inflammation.
- Recognizing symptoms of sciatica, such as radiating pain and tingling, is vital for seeking timely treatment.
- Understanding radiculopathy is key to managing pain effectively and improving quality of life.
How Degenerative Disc Disease Leads to Sciatica Pain
Understanding the common mechanisms and symptoms linking Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) to sciatica can help in identifying and managing the condition effectively.
Mechanisms: How DDD Triggers Sciatica
-
•
Disc Herniation: Disc bulges or ruptures, pressing on nerves.
-
•
Bone Spurs: Degeneration leads to bone growths that compress nerves.
-
•
Inflammation: Tissue inflammation irritates surrounding nerves.
Key Symptoms of Sciatica (Linked to DDD)
-
•
Radiating Pain: Pain from lower back down through buttock and leg.
-
•
Tingling/Numbness: Pins and needles sensation in the affected leg.
-
•
Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the leg or foot, affecting movement.
Understanding Degenerative Disc Disease and Its Connection to Sciatica
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is a common condition that affects many individuals, particularly as they age. This term can be a bit misleading since it implies a disease, but it actually refers to the natural wear and tear of the intervertebral discs in our spine. Have you ever wondered why you feel stiffness or pain in your back after sitting for too long? Understanding DDD can help you make sense of these sensations, especially in connection with sciatica.
DDD occurs when the discs lose hydration and elasticity over time, which can lead to a range of issues, including pain and discomfort. In my experience as a physiotherapist, I've seen many patients struggle with DDD, and understanding its impact on the body is crucial for effective management and treatment.
What is Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)?
Degenerative Disc Disease isn't actually classified as a disease in the traditional sense but rather a condition resulting from disc degeneration. The discs act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae, providing both flexibility and stability to our spine. Symptoms can vary widely, from mild discomfort to severe pain, which can significantly affect your quality of life.
- Natural wear and tear due to aging
- Genetics, which can predispose individuals to faster degeneration
- Injuries or trauma that exacerbate the condition
By recognizing these factors, you gain insight into your own experience with back pain. This knowledge can empower you to pursue appropriate treatment options and lifestyle changes that support your spine health.
The Role of Intervertebral Discs: Structure and Function
The intervertebral discs play a vital role in maintaining proper spinal function. Each disc consists of a tough outer layer known as the annulus fibrosus and a gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus. Together, they allow for movement, provide cushioning, and help maintain proper alignment of the spine. When these discs begin to deteriorate, they lose their ability to absorb shock, which can lead to discomfort and even sciatica.
- Flexibility: Discs allow for motion and bending of the spine.
- Shock Absorption: They cushion the vertebrae during movement.
- Stability: Discs help maintain the alignment of the spine.
Understanding the structure and function of these discs can help you appreciate the importance of keeping them healthy. Simple exercises and good posture can go a long way!
Spinal Degeneration: Causes and Effects on Health
Spinal degeneration occurs naturally as we age, but certain factors can accelerate the process. These factors include lifestyle habits such as poor posture, lack of exercise, and obesity. Each of these can put extra strain on your spine, leading to increased wear and tear on the discs. Research highlighted in Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology emphasizes the connection between various biomechanical factors and spinal health.
- Poor posture can compress discs and lead to faster degeneration.
- A sedentary lifestyle reduces blood flow and nutrients to the discs.
- Obesity adds excess weight that strains the spine.
Recognizing these causes can be the first step toward making necessary lifestyle changes. Small adjustments, like incorporating regular activity and improving your posture, can significantly impact your spinal health!
Pro Tip
Did you know? Incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises into your daily routine can significantly alleviate the symptoms associated with Degenerative Disc Disease and sciatica. Focus on exercises that enhance flexibility and strengthen your core muscles to support your spine better.
How Degenerative Disc Disease Triggers Sciatica Pain
Understanding how Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) can lead to sciatica pain is crucial for effective management. As a physiotherapist with over a decade of experience, I’ve seen countless individuals struggle with this connection. So, how exactly does DDD contribute to nerve compression and subsequent sciatic pain? Let’s explore this together!
DDD occurs when the intervertebral discs in your spine begin to break down, which can lead to changes in spinal alignment and increased pressure on nearby nerves. When these discs degrade, they can lose their cushioning ability, leading to conditions that result in nerve irritation or compression. This is where the link to sciatica becomes significant.
The Mechanism: How DDD Leads to Nerve Compression
To understand the connection between DDD and sciatica, we need to look at the mechanisms at play. When the cushioning between the vertebrae wears down, it can affect the spinal structure in several ways, potentially leading to pain and mobility issues.
- Disc Herniation: A disc may bulge or rupture, pressing against nearby nerves.
- Bone Spurs: As discs degenerate, the body may form bone spurs that can further compress nerves.
- Inflammation: Degeneration can lead to inflammation of surrounding tissues, which may irritate nerves.
Each of these mechanisms can contribute to that nagging pain running down your leg. If you’ve ever felt a sharp pain or tingling sensation, you might be experiencing these effects firsthand!
Identifying Symptoms of Sciatica Linked to DDD
Recognizing the symptoms of sciatica related to DDD is essential for you to seek timely treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- Radiating Pain: Pain that travels from your lower back down through your buttock and leg.
- Tingling or Numbness: A sensation of pins and needles in the affected leg.
- Muscle Weakness: A feeling of weakness in the leg or foot, affecting your ability to move.
These symptoms can vary in intensity, and understanding them can help you communicate effectively with your healthcare provider. Have you experienced any of these signs? It's always best to address them early!
Understanding Radiculopathy and Its Relation to Sciatica
Radiculopathy is a term that may come up when discussing sciatica and DDD. It refers to the irritation or compression of nerve roots as they exit the spine. In cases of DDD, this often occurs due to the changes happening in the discs or surrounding vertebrae.
Here are some key points to grasp about radiculopathy and its connection to sciatic pain:
- Location Matters: Depending on which nerve root is affected, the pain and symptoms can differ.
- Diagnostic Importance: Identifying radiculopathy can help pinpoint the source of pain and guide treatment.
- Proactive Management: Early intervention can prevent worsening symptoms and improve your quality of life.
As you learn more about your condition, remember that understanding radiculopathy is a step toward taking control of your spine health. Have you talked to a specialist about your symptoms? Gaining clarity can empower your recovery journey!
Frequently Asked Questions About DDD and Sciatica
- 1. Is Degenerative Disc Disease truly a disease?
- No, it's not a disease in the traditional sense, but rather a natural process of wear and tear on the spinal discs that occurs with aging. It can lead to symptoms like pain and stiffness.
- 2. How do intervertebral discs contribute to spinal health?
- Intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers, providing flexibility and stability to the spine. They allow for movement, cushion the vertebrae, and help maintain proper spinal alignment.
- 3. What lifestyle factors can worsen spinal degeneration?
- Poor posture, a sedentary lifestyle, and obesity can accelerate spinal degeneration by putting extra strain on the discs and reducing nutrient flow to them.
- 4. How does DDD lead to sciatica?
- DDD can lead to sciatica through various mechanisms, including disc herniation (where a disc bulges or ruptures and presses on nerves), bone spurs (bone growths that compress nerves), and inflammation of surrounding tissues that irritate nerves.
- 5. What are the common symptoms of sciatica linked to DDD?
- Common symptoms include radiating pain from the lower back down the buttock and leg, tingling or numbness (pins and needles sensation) in the affected leg, and muscle weakness in the leg or foot.
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Understanding DDD: Degenerative Disc Disease is a natural wear and tear of spinal discs, not a disease in the traditional sense.
- Symptoms to Watch For: Symptoms of DDD can include pain, stiffness, and discomfort in the back, with sciatica being a common complication.
- Causes of Spinal Degeneration: Factors such as poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity can accelerate degeneration.
- Effects on Nerve Compression: DDD can lead to conditions like disc herniation and bone spurs, which may compress nerves and trigger sciatica pain.
- Identifying Sciatica Symptoms: Look for symptoms like radiating pain, tingling, and muscle weakness as signs of sciatica related to DDD.
- Importance of Early Intervention: Recognizing symptoms early can lead to better management and improved quality of life.




Stress and Sciatica: Finding Relief
Preparing for Sciatica Surgery: Essentials
Aquatic Therapy for Sciatica Recovery
Exploring Sciatica Medication Options
Ergonomic Solutions for Sciatica Relief